Upload folder using huggingface_hub
Browse files- dev_to_blog_post.md +210 -0
dev_to_blog_post.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
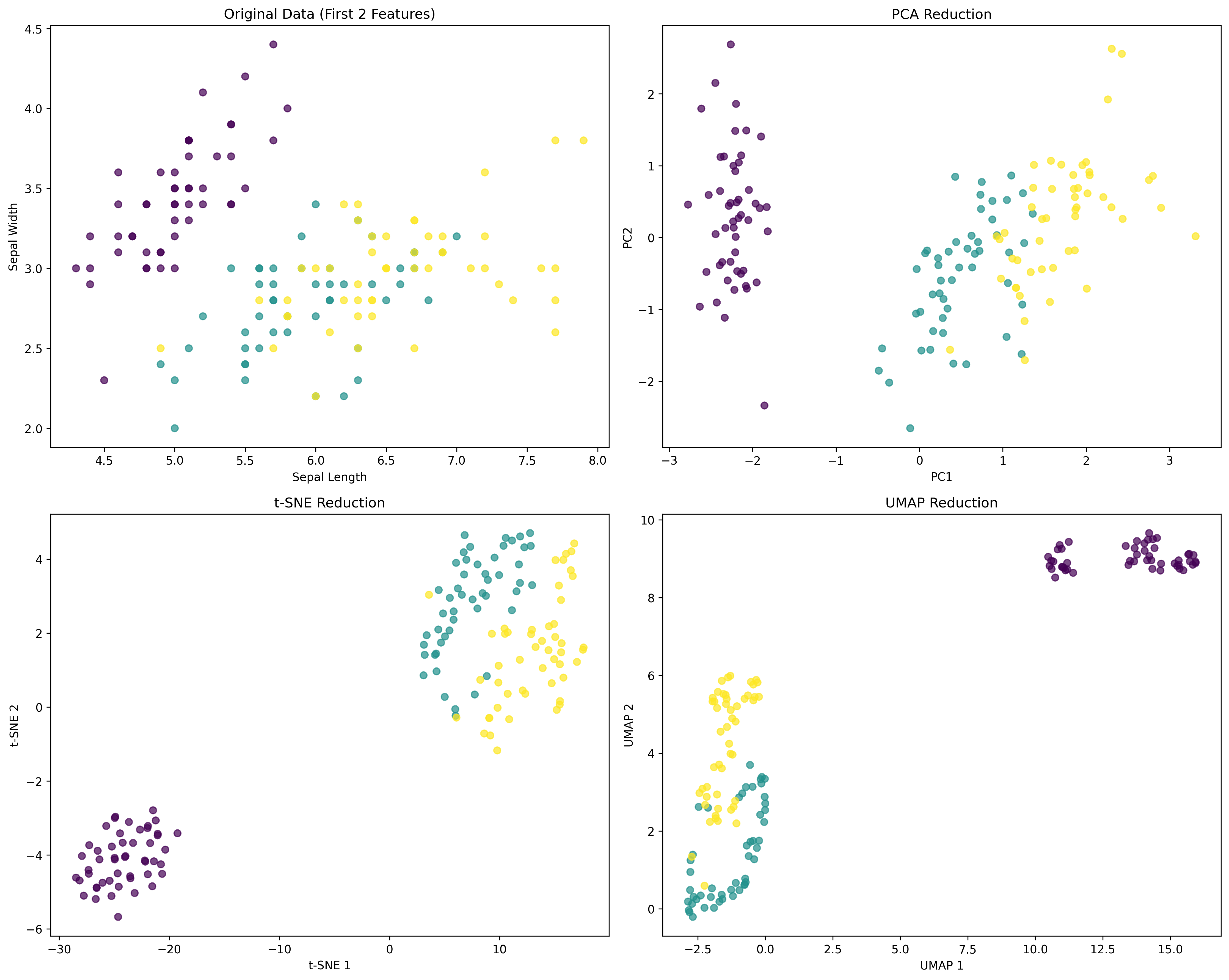
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
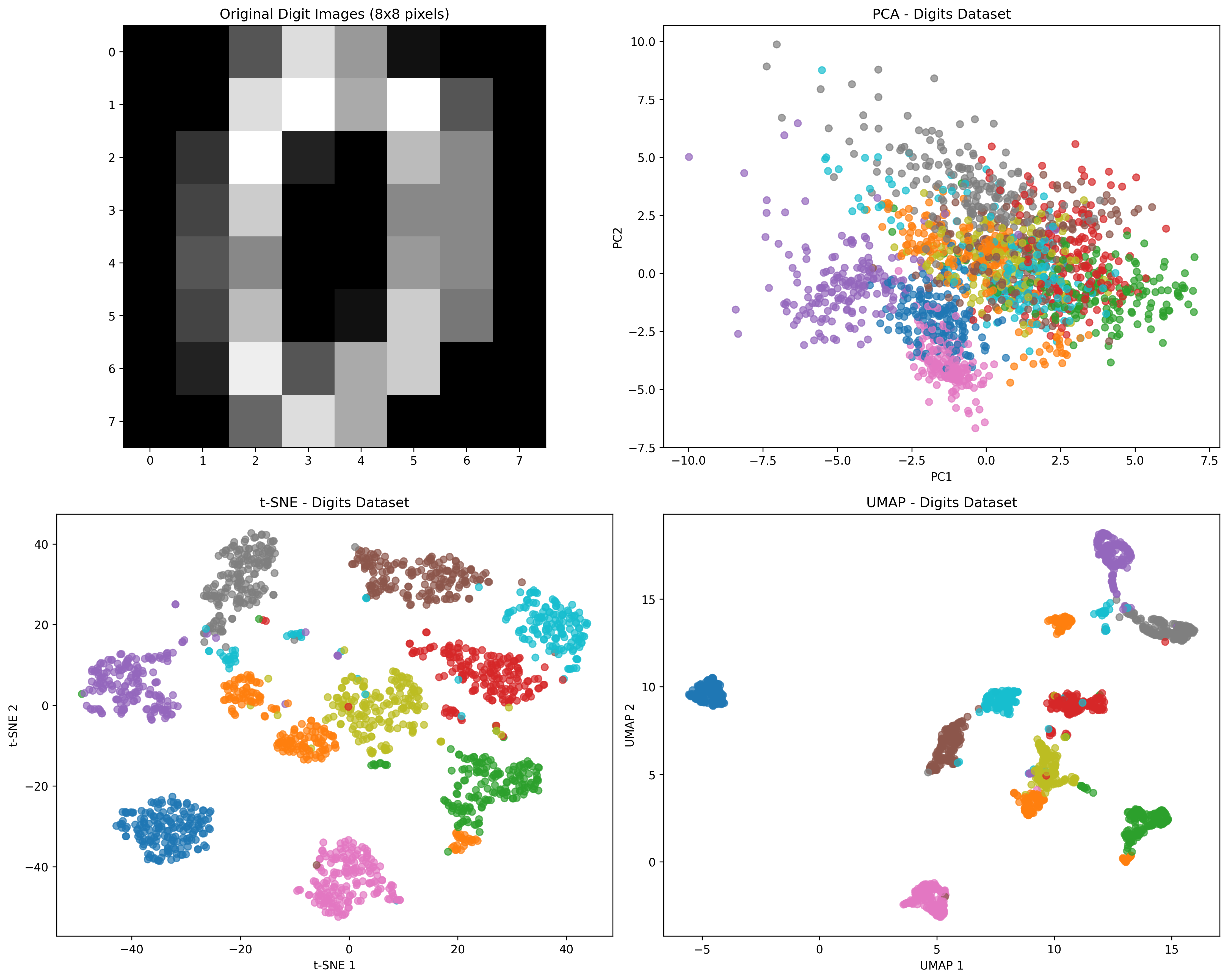
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
---
|
| 2 |
+
title: "Mastering Dimensionality Reduction: A Comprehensive Guide to PCA, t-SNE, UMAP, and Autoencoders"
|
| 3 |
+
published: true
|
| 4 |
+
description: "A complete implementation and analysis of dimensionality reduction techniques with practical examples, performance comparisons, and when to use each method."
|
| 5 |
+
tags: machinelearning, datascience, python, dimensionalityreduction
|
| 6 |
+
cover_image: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GruheshKurra/dimensionality-reduction/main/visualizations/iris_comparison.png
|
| 7 |
+
canonical_url:
|
| 8 |
+
---
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
# Mastering Dimensionality Reduction: A Comprehensive Guide to PCA, t-SNE, UMAP, and Autoencoders
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
Dimensionality reduction is like taking a 3D object and creating a 2D shadow that preserves the most important information. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore four powerful techniques: PCA, t-SNE, UMAP, and Autoencoders, with complete implementations and performance analysis.
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
## 🎯 Why Dimensionality Reduction Matters
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
Imagine you have a dataset with 1000 features describing each data point, but many features are redundant or noisy. Dimensionality reduction helps you:
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
- **Visualize High-Dimensional Data**: Plot complex datasets in 2D/3D
|
| 19 |
+
- **Reduce Computational Complexity**: Faster processing with fewer features
|
| 20 |
+
- **Eliminate Noise**: Remove redundant or noisy features
|
| 21 |
+
- **Overcome Curse of Dimensionality**: Improve algorithm performance
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
## 📊 The Four Techniques We'll Compare
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
### 1. **PCA (Principal Component Analysis)**
|
| 26 |
+
- **Type**: Linear transformation
|
| 27 |
+
- **Best For**: Data with linear relationships
|
| 28 |
+
- **Key Advantage**: Interpretable components, fast computation
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
### 2. **t-SNE (t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding)**
|
| 31 |
+
- **Type**: Non-linear manifold learning
|
| 32 |
+
- **Best For**: Data visualization and clustering
|
| 33 |
+
- **Key Advantage**: Excellent at preserving local structure
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
### 3. **UMAP (Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection)**
|
| 36 |
+
- **Type**: Non-linear manifold learning
|
| 37 |
+
- **Best For**: Balanced local and global structure preservation
|
| 38 |
+
- **Key Advantage**: Faster than t-SNE, better global structure
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
### 4. **Autoencoders**
|
| 41 |
+
- **Type**: Neural network approach
|
| 42 |
+
- **Best For**: Complex non-linear relationships
|
| 43 |
+
- **Key Advantage**: Highly flexible, customizable architecture
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
## 🔬 Experimental Setup
|
| 46 |
+
|
| 47 |
+
I tested all four methods on two standard datasets:
|
| 48 |
+
- **Iris Dataset**: 150 samples, 4 features, 3 classes (low-dimensional)
|
| 49 |
+
- **Digits Dataset**: 1797 samples, 64 features, 10 classes (high-dimensional)
|
| 50 |
+
|
| 51 |
+
## 📈 Performance Results
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
Here's how each method performed in terms of **accuracy retention** (classification performance after dimensionality reduction):
|
| 54 |
+
|
| 55 |
+
### Iris Dataset Results
|
| 56 |
+
| Method | Accuracy Retention |
|
| 57 |
+
|--------|-------------------|
|
| 58 |
+
| PCA | 97.5% |
|
| 59 |
+
| t-SNE | 105.0% |
|
| 60 |
+
| UMAP | 102.5% |
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
### Digits Dataset Results
|
| 63 |
+
| Method | Accuracy Retention |
|
| 64 |
+
|--------|-------------------|
|
| 65 |
+
| PCA | 52.4% |
|
| 66 |
+
| t-SNE | 100.4% |
|
| 67 |
+
| UMAP | 99.2% |
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
## 💡 Key Insights
|
| 70 |
+
|
| 71 |
+
### 1. **PCA Works Best for Linear Data**
|
| 72 |
+
```python
|
| 73 |
+
# PCA explained variance for Iris dataset
|
| 74 |
+
iris_pca_variance = [73.0%, 22.9%] # First 2 components explain 95.9%
|
| 75 |
+
digits_pca_variance = [12.0%, 9.6%] # First 2 components explain only 21.6%
|
| 76 |
+
```
|
| 77 |
+
|
| 78 |
+
PCA excelled on the Iris dataset but struggled with the high-dimensional Digits dataset, showing its linear nature.
|
| 79 |
+
|
| 80 |
+
### 2. **t-SNE Excels at Visualization**
|
| 81 |
+
t-SNE sometimes even improved classification performance! This happens because it's excellent at separating clusters, making classification easier.
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
### 3. **UMAP Provides the Best Balance**
|
| 84 |
+
UMAP consistently delivered excellent performance across both datasets, proving its effectiveness for both visualization and downstream tasks.
|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
### 4. **Autoencoders Are Highly Flexible**
|
| 87 |
+
Our neural network autoencoder achieved good reconstruction with final losses of:
|
| 88 |
+
- Iris: 0.081 (excellent)
|
| 89 |
+
- Digits: 0.348 (good, considering complexity)
|
| 90 |
+
|
| 91 |
+
## 🛠️ Implementation Highlights
|
| 92 |
+
|
| 93 |
+
### Simple Autoencoder Architecture
|
| 94 |
+
```python
|
| 95 |
+
class SimpleAutoencoder(nn.Module):
|
| 96 |
+
def __init__(self, input_dim, encoding_dim):
|
| 97 |
+
super().__init__()
|
| 98 |
+
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
|
| 99 |
+
nn.Linear(input_dim, 128),
|
| 100 |
+
nn.ReLU(),
|
| 101 |
+
nn.Linear(128, 64),
|
| 102 |
+
nn.ReLU(),
|
| 103 |
+
nn.Linear(64, encoding_dim)
|
| 104 |
+
)
|
| 105 |
+
|
| 106 |
+
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
|
| 107 |
+
nn.Linear(encoding_dim, 64),
|
| 108 |
+
nn.ReLU(),
|
| 109 |
+
nn.Linear(64, 128),
|
| 110 |
+
nn.ReLU(),
|
| 111 |
+
nn.Linear(128, input_dim)
|
| 112 |
+
)
|
| 113 |
+
```
|
| 114 |
+
|
| 115 |
+
### Evaluation Strategy
|
| 116 |
+
```python
|
| 117 |
+
def evaluate_dimensionality_reduction(original_data, reduced_data, target):
|
| 118 |
+
# Train classifiers on both original and reduced data
|
| 119 |
+
rf_orig = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
|
| 120 |
+
rf_red = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
# Compare accuracy retention
|
| 123 |
+
acc_orig = accuracy_score(y_test, rf_orig.predict(X_test_orig))
|
| 124 |
+
acc_red = accuracy_score(y_test, rf_red.predict(X_test_red))
|
| 125 |
+
|
| 126 |
+
return (acc_red/acc_orig) * 100 # Accuracy retention percentage
|
| 127 |
+
```
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
## 🎨 Visualization Results
|
| 130 |
+
|
| 131 |
+
The visualizations clearly show the differences between methods:
|
| 132 |
+
|
| 133 |
+
|
| 134 |
+
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
## 🚀 When to Use Each Method
|
| 138 |
+
|
| 139 |
+
### Use **PCA** when:
|
| 140 |
+
- ✅ You need interpretable components
|
| 141 |
+
- ✅ Data has linear relationships
|
| 142 |
+
- ✅ You want fast computation
|
| 143 |
+
- ✅ Feature compression is the goal
|
| 144 |
+
|
| 145 |
+
### Use **t-SNE** when:
|
| 146 |
+
- ✅ Visualization is the primary goal
|
| 147 |
+
- ✅ You have small to medium datasets
|
| 148 |
+
- ✅ Local structure preservation is crucial
|
| 149 |
+
- ❌ Avoid for very large datasets (slow)
|
| 150 |
+
|
| 151 |
+
### Use **UMAP** when:
|
| 152 |
+
- ✅ You need both local and global structure
|
| 153 |
+
- ✅ You have large datasets
|
| 154 |
+
- ✅ You want to transform new data points
|
| 155 |
+
- ✅ General-purpose dimensionality reduction
|
| 156 |
+
|
| 157 |
+
### Use **Autoencoders** when:
|
| 158 |
+
- ✅ You have complex non-linear relationships
|
| 159 |
+
- ✅ You need custom architectures
|
| 160 |
+
- ✅ You have sufficient computational resources
|
| 161 |
+
- ✅ You want to learn representations for specific tasks
|
| 162 |
+
|
| 163 |
+
## 📊 Method Comparison Summary
|
| 164 |
+
|
| 165 |
+
| Aspect | PCA | t-SNE | UMAP | Autoencoder |
|
| 166 |
+
|--------|-----|-------|------|-------------|
|
| 167 |
+
| **Linearity** | Linear | Non-linear | Non-linear | Non-linear |
|
| 168 |
+
| **Speed** | Fast | Slow | Medium | Medium |
|
| 169 |
+
| **Deterministic** | Yes | No | Yes* | Yes* |
|
| 170 |
+
| **New Data** | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
| 171 |
+
| **Interpretability** | High | Low | Medium | Low |
|
| 172 |
+
| **Scalability** | Excellent | Poor | Good | Good |
|
| 173 |
+
|
| 174 |
+
*With fixed random seed
|
| 175 |
+
|
| 176 |
+
## 🛠️ Complete Implementation
|
| 177 |
+
|
| 178 |
+
The complete implementation includes:
|
| 179 |
+
- 📖 Detailed theory explanations with mathematical foundations
|
| 180 |
+
- 💻 Step-by-step code with comprehensive comments
|
| 181 |
+
- 📊 Performance evaluation framework
|
| 182 |
+
- 🎨 Visualization suite for method comparison
|
| 183 |
+
- 💾 Model persistence for reusability
|
| 184 |
+
|
| 185 |
+
## 🔗 Access the Complete Code
|
| 186 |
+
|
| 187 |
+
- **GitHub Repository**: [dimensionality-reduction](https://github.com/GruheshKurra/dimensionality-reduction)
|
| 188 |
+
- **Hugging Face**: [karthik-2905/dimensionality-reduction](https://huggingface.co/karthik-2905/dimensionality-reduction)
|
| 189 |
+
- **Interactive Notebook**: Available in the repository
|
| 190 |
+
|
| 191 |
+
## 💭 Key Takeaways
|
| 192 |
+
|
| 193 |
+
1. **No One-Size-Fits-All**: Each method has its strengths and optimal use cases
|
| 194 |
+
2. **Data Matters**: The nature of your data significantly impacts method selection
|
| 195 |
+
3. **Evaluation is Crucial**: Always evaluate dimensionality reduction quality using downstream tasks
|
| 196 |
+
4. **Visualization vs. Performance**: Methods that create beautiful visualizations might not always preserve the most information for machine learning tasks
|
| 197 |
+
|
| 198 |
+
## 🎯 Next Steps
|
| 199 |
+
|
| 200 |
+
Try implementing these techniques on your own datasets! Consider:
|
| 201 |
+
- Experimenting with different hyperparameters
|
| 202 |
+
- Combining multiple methods in a pipeline
|
| 203 |
+
- Using dimensionality reduction as preprocessing for other ML tasks
|
| 204 |
+
- Exploring advanced variants like Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
|
| 205 |
+
|
| 206 |
+
---
|
| 207 |
+
|
| 208 |
+
*What's your experience with dimensionality reduction? Which method works best for your use case? Share your thoughts in the comments below!*
|
| 209 |
+
|
| 210 |
+
**Tags**: #MachineLearning #DataScience #Python #DimensionalityReduction #PCA #tSNE #UMAP #Autoencoders #DataVisualization
|